A member of the population’s “resiliency”, or ability to respond to and recover from the impacts of flooding, differs greatly depending on a variety of factors including income, financial and social capacity, age, mobility, cultural and linguistic isolation and constraints, local public support systems, physical and psychological challenges, and other factors. These factors can reduce resiliency and create vulnerability for individuals, families, neighborhoods, and communities. The most vulnerable populations are particularly at risk and will have a more difficult time recovering from the impacts of flooding. Their vulnerability creates community-wide vulnerability. Recognizing the challenges that these populations face is the first step to improving watershed resiliency and reducing the impact of flooding on individuals, families, neighborhoods, and communities, including those that are least able to recover.
Through the Iowa Watershed Approach, the UWR WMA and their partners are working with the Resiliency Team from the University of Iowa to better understand resiliency issues in the UWR Watershed and identify ways to reduce the impact of flooding on the most vulnerable UWR Watershed residents.
Vulnerable Populations in the Upper Wapsipinicon River Watershed
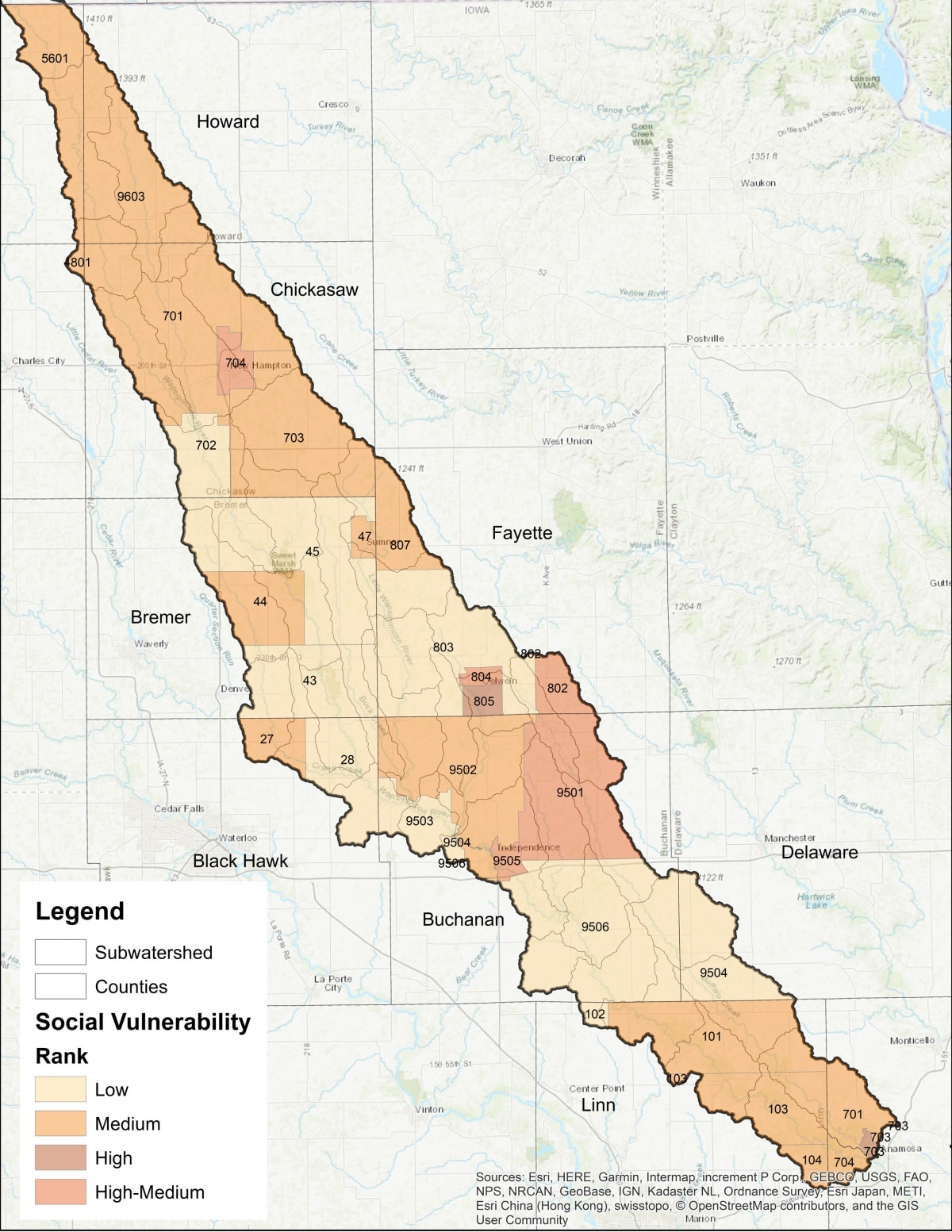
The Iowa Flood Center analysed socially vulnerable populations in all of the Iowa Watershed Approach watersheds, including the UWR Watershed. The Social Vulnerability Maps identify areas with high social vulnerability, which correlates with low resilience to disasters particularly flood disasters. The social vulnerability data combines a percentage of 12 indicators from the U.S. Census Bureau including; African American, language barrier, renters, unemployed, poverty, children, elderly, Hispanic, low education, female-headed households, disables, and no vehicle access.
Social Vulnerability of Census Tracts
Top Three Indicators for Social Vulnerability by Census Tract
The table below is correlated with the map and shows the top three indicators for social vulnerability for each Census Tract in the UWR Watershed. To explore more about social vulnerability in the UWR Watershed and other Iowa Watershed Approach watersheds explore the Iowa Watershed Information System
| Census Tract | County | Social Vulnerability Rating | Total Population | 1st Indicator | 2nd Indicator | 3rd Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 805 | Fayette | High | 3709 | % Hispanic or Latino | % Female Head of Household | % No High School Diploma |
| 703 | Jones | High | 4787 | % Black or African American | % Unemployed | % Renter |
| 704 | Chickasaw | High-Medium | 3786 | % Disabled | % No High School Diploma | % Renter |
| 9505 | Buchanan | High-Medium | 3943 | % Female Head of Household | % No Vehicle Access | % Hispanic or Latino |
| 804 | Fayette | High-Medium | 2658 | % Disabled | % Hispanic or Latino | % Renter |
| 802 | Fayette | High-Medium | 3303 | % Poverty | % Unemployed | % Limited English |
| 9501 | Buchanan | High-Medium | 2466 | % Children | % Unemployed | % Poverty |
| 9502 | Buchanan | Medium | 3682 | % No Vehicle Access | % Children | % No High School Diploma |
| 5601 | Mitchell | Medium | 3506 | % Limited English | % No High School Diploma | % Children |
| 704 | Jones | Medium | 4712 | % Disabled | % Female Head of Household | % Unemployed |
| 401 | Chickasaw | Medium | 3170 | % Limited English | % Hispanic or Latino | % No High School Diploma |
| 47 | Bremer | Medium | 2232 | % Age 65 or Older | % Disabled | % Children |
| 807 | Fayette | Medium | 3154 | % Children | % No High School Diploma | % Age 65 or Older |
| 9603 | Howard | Medium | 2842 | % No High School Diploma | % No Vehicle Access | % Children |
| 104 | Linn | Medium | 2722 | % Limited English | % Unemployed | % Children |
| 703 | Chickasaw | Medium | 2802 | % Female Head of Household | % Children | % Age 65 or Older |
| 701 | Jones | Medium | 4180 | % Female Head of Household | % Children | % Hispanic or Latino |
| 101 | Linn | Medium | 3084 | % Children | % Unemployed | % Renter |
| 44 | Bremer | Medium | 2898 | % Age 65 or Older | % Hispanic or Latino | % Female Head of Household |
| 27 | Black Hawk | Medium | 3980 | % Disabled | % No High School Diploma | % Unemployed |
| 9504 | Buchanan | Medium | 2809 | % Limited English | % Age 65 or Older | % No Vehicle Access |
| 103 | Linn | Medium | 3809 | % Children | % Female Head of Household | % Unemployed |
| 4801 | Floyd | Medium | 3024 | % Limited English | % Children | % No High School Diploma |
| 702 | Chickasaw | Low-Medium | 2406 | % Disabled | % Unemployed | % Age 65 or Older |
| 9504 | Delaware | Low-Medium | 5225 | % Unemployed | % Children | % No High School Diploma |
| 9503 | Buchanan | Low-Medium | 3614 | % Unemployed | % Children | % Female Head of Household |
| 45 | Bremer | Low-Medium | 2679 | % Unemployed | % Hispanic or Latino | % Limited English |
| 9506 | Buchanan | Low-Medium | 4517 | % Children | % Age 65 or Older | % Renter |
| 28 | Black Hawk | Low-Medium | 3224 | % Children | % Female Head of Household | % Hispanic or Latino |
| 43 | Bremer | Low-Medium | 1683 | % Children | % Hispanic or Latino | % Age 65 or Older |
| 803 | Fayette | Low-Medium | 2449 | % Children | % Unemployed | % Age 65 or Older |
| 102 | Linn | Low-Medium | 4440 | % Children | % Unemployed | % No Vehicle Access |